California was warned about climate change 30 years ago Now it's feeling the effects Los Angeles Times
Table Of Content
Other sourcesThis category includes emissions from energy-related activities other than fossil fuel combustion, such as the extraction, refining, processing, and transportation of oil, gas, and coal. Globally, according to the IPCC, this sector accounts for 9.6 percent of emissions. The greenhouse effect is the natural warming of the earth that results when gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun that would otherwise escape into space.
California man first in U.S. charged with smuggling greenhouse gases - Axios
California man first in U.S. charged with smuggling greenhouse gases.
Posted: Mon, 04 Mar 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Radiative balance

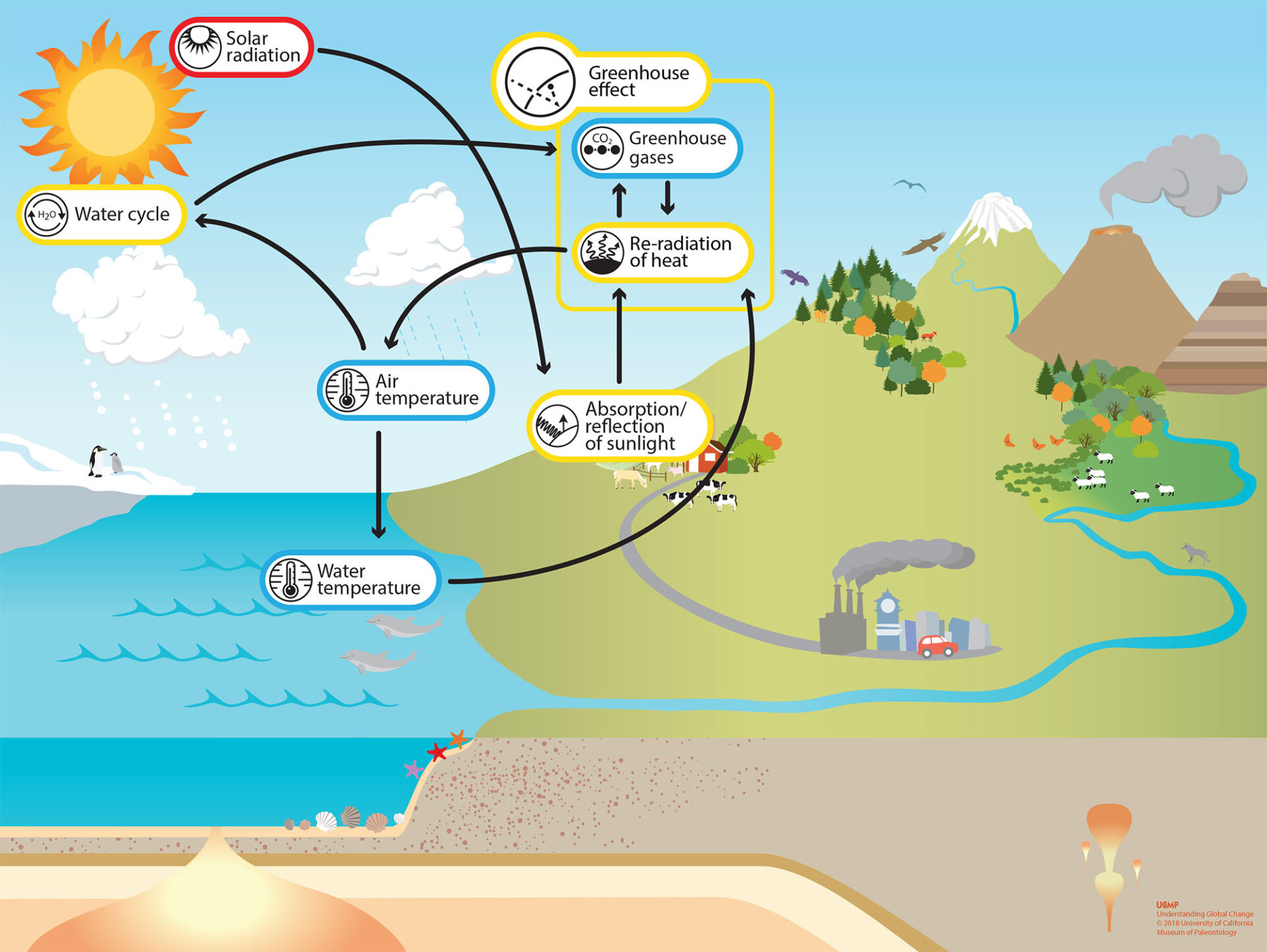
Fluorinated gases are only destroyed by sunlight in the far upper atmosphere. Humans directly affect the greenhouse effect through activities that result in greenhouse gas emissions. The Earth system model below includes some of the ways that human activities increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Releasing greenhouse gases intensifies the greenhouse effect, and increases Earth’s average air temperatures (also known as global warming). Hover over or click on the icons to learn more about these human causes of change and how they influence the greenhouse effect.
What are the major causes of the greenhouse effect?
Some greenhouse gases come from natural sources, for example, evaporation adds water vapor to the atmosphere. Animals and plants release carbon dioxide when they respire, or breathe. There is evidence that suggests methane is released in low-oxygen environments, such as swamps or landfills. Volcanoes—both on land and under the ocean—release greenhouse gases, so periods of high volcanic activity tend to be warmer.
A Couple of Common Greenhouse Gases
In fact, the paths to halting global temperature increases of 1.5 or 2 degrees C, the two goals outlined by the IPCC, rely in some way on adopting methods of sucking CO2 from the sky. Those include planting trees, conserving existing forests and grasslands, and capturing CO2 from power plants and factories. The atmosphere near the Earth's surface is largely opaque to longwave radiation and most heat loss from the surface is by evaporation and convection. However radiative energy losses become increasingly important higher in the atmosphere, largely because of the decreasing concentration of water vapor, an important greenhouse gas.
Replacing these HFCs and properly disposing of them is considered to be one of the most important climate actions the world can take. "If cirrus clouds behave like a blanket around the Earth, you're trying to get rid of that blanket," Lohmann, a professor of experimental atmospheric physics at ETH Zurich, told Live Science. Geoengineering Is Easier Said Than Done] "You remove the water vapor, you remove the humidity and you prevent the normal cirrus cloud formation," Lohmann said. The movie clip below shows the ozone measurements after computers have processed them into images. In some places that red area is high in the stratosphere where it shows "good ozone," but in other places (such over large cities), the red areas drop to very close to the ground, showing "bad ozone." That's one reason NASA has developed the Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer, or TES.
Others, like CO2, largely result from natural processes like respiration, and from the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. With the increase in population, the utilization of fossil fuels has increased. This has led to an increase in the release of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. At night, when the earth cools down the heat is radiated back into the atmosphere. During this process, the heat is absorbed by the greenhouse gases in the earth’s atmosphere. This is what makes the surface of the earth warmer, that makes the survival of living beings on earth possible.
Graphic: Major Greenhouse Gas Sources, Lifespans, and Possible Added Heat - Science@NASA
Graphic: Major Greenhouse Gas Sources, Lifespans, and Possible Added Heat.
Posted: Thu, 22 Jun 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Some, such as tectonic activities, operate at timescales of millions of years, whereas others, such as vegetation, soil, wetland, and ocean sources and sinks, operate at timescales of hundreds to thousands of years. Since the start of the Industrial Revolution in the mid-18th century, human activities have greatly increased the concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Consequently, measured atmospheric concentrations of CO2 are many times higher than pre-industrial levels. About half of the sun’s radiation that travels toward the earth never makes it to the earth’s surface. Clouds and the atmosphere reflect about one-third of the radiation back toward the sun, and they also absorb another 20 percent. The rest of the radiation—about 50 percent—reaches the earth, where it is absorbed by oceans and land.

Global Change Infographic
This process releases up to 4.8 billion metric tons of carbon into the atmosphere every year, according to the World Resources Institute. BGS is committed to research aimed at slowing down the effects of a changing climate, whilst helping society to become resilient to climate change. Tell President Biden and Congress to slash climate pollution and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. Shifting to renewable energy, putting a price on carbon, and phasing out coal are all important elements in reducing GHG emissions.
In addition to these natural compounds, synthetic fluorinated gases also function as greenhouse gases. Different greenhouse gases have different chemical properties and are removed from the atmosphere, over time, by various processes. Carbon dioxide, for example, is absorbed by “carbon sinks” such as forests, soil, and the ocean.
To learn more about what is the greenhouse effect, its definition, causes and effects, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download the BYJU’S app for further reference. Nitrous oxide used in fertilizers is one of the contributors to the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere. Geological records demonstrate that there have been a number of large variations in Earth’s climate in the past. Aerosols also have a detrimental impact on human health and affect other parts of the climate system, such as rainfall. Nationwide, cars and trucks are responsible for more than half of the transportation-related carbon emissions.
Greenhouse gases consist of carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons, and water vapor. Water vapor, which reacts to temperature changes, is referred to as a 'feedback', because it amplifies the effect of forces that initially caused the warming. Other anthropogenic sources include the burning of forests and the clearing of land. Anthropogenic emissions currently account for the annual release of about 7 gigatons (7 billion tons) of carbon into the atmosphere.
That's at least 2.8 million years before modern humans roamed the planet. Fossils show that forests grew in the Canadian Arctic during the Pliocene, and savannas and woodlands spread over what's now the Sahara desert. The surface of the Earth absorbs just under half of the sun’s energy, while the atmosphere absorbs 23 per cent, and the rest is reflected back into space. Natural processes ensure that the amount of incoming and outgoing energy is equal, keeping the planet’s temperature stable. The greenhouse effect describes a similar phenomenon on a planetary scale but, instead of the glass of a greenhouse, certain gases are increasingly raising global temperatures.
Comments
Post a Comment